Breadcrumbs
How to reset Static IP Addresses to Dynamic IP Addresses
Every computer that connects to the internet must have what is called an IP address (Internet Protocol address). The IP address is a computer's identity on a network. Without this unique address, there is no identity and therefore no connectivity. IP addresses are a series of four numbers, each ranging between 0 and 253. For example, the address of a typical computer might look something like this:
192.168.1.217
There are two ways that a computer is assigned an IP address. First, it can be done manually. This is called a fixed, or static, IP address. Static IPs are usually assigned by a network administrator who needs control over the computers in a local area network in order to manage them. The second way a computer receives an IP address is when it is automatically assigned by a router. A router is a network device that manages network traffic in a local area, chief among its tasks being to share an internet connection with more than one computer at a time. Dynamic IP addresses, on the other hand, change quite often. They are leased for periods of time to the computers and devices connected to them. In fact, each time your notebook, tablet or smartphone connects to your home network it could be given a different IP address by your router. As well, the IP address your notebook, tablet or cell phone receives from your router at home will change again when you connect to a wireless hotspot at a coffee shop, hotel or even a friend's house. It is the router's job to assign all the IP addresses of the devices that are using its network, and then to manage the traffic that is appropriate to each device's requests on the network and on the internet that goes beyond its local network.
Internet connectivity is blocked, however, when a computer device has been set with a static IP address and a router cannot manage it on its network. Routers do not have permission to change the static address of a computer once it has been set. If a particular computer's static address is not within the range of addresses over which a router has control, then that computer will not be allowed to connect to the internet. Once again, your web browser will greet you with the dreaded Page cannot be found message. So, if the problem is due to a static IP, a solution can be easily applied.
Static IP addresses can be inserted without the knowledge of the user by a virus attack, as the virus attempts to steer the infected computer to its own website. Sometimes, mishandled installations of routers with configuration CDs can be the source of the problem. Regardless of the reason for the unwanted configuration, static IP addresses can be easily removed. Though there are several ways to do this within each Windows operating system, following these steps will get you to the configuration page where IP addresses can be changed:
Opening the Windows Network Properties window:
Windows 7:
- Right-click the wired or wireless network icon in the system tray.
- Click Open Network and Sharing Center in the menu.
- In the left panel, click Change adapter settings.
- Right-click the adapter you use to connect to the internet.
- Click Properties in the drop-down menu.
Windows 8:
- Open the Charms icon list.
- Click on the Search charm.
- Among the search options (Apps, Settings, Files), click on Settings.
- In the search window, type IP.
- In the results in the upper left, click on View Network Connections.
- Depending on your connection choice, right click either Ethernet or Wireless adapter.
- Click Properties in the drop-down menu.
Opening the TCP/IP Properties page:
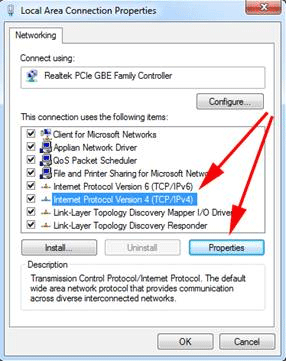
In Windows 7 and Windows 8, you will see a window that looks something like the example below with TCP/IPv4. Click on the protocol for your operating system, then click Properties as indicated by the arrows.
Examining the IP address settings:
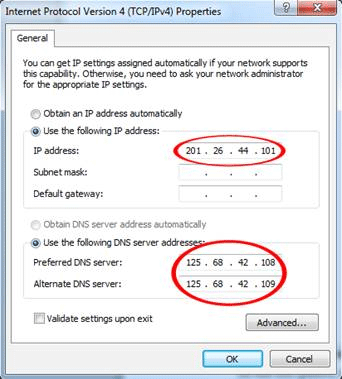
If it turns out that IP addresses are fixed (static) then numbers will be entered in the box for IP address and also perhaps for other boxes in this window (circled, on the left). The point is that if ANY numbers are inserted at all, then the IP address for this computer has been fixed, and a router in a home, office or public place that is trying to assign dynamic addresses will not be able to do so. Thus, the computer will not be able to connect freely to the internet.
It may be the case, however, that your computer is in a managed network (such as in a business office) that has been set up by an authorized network administrator. In such a situation - and if access to such settings has not been locked out - these addresses may need to be left as they are. Change them only if you are not in a managed network. If you are not in a managed network, then go to the next step.
Clearing the static IPs and resetting to dynamic IPs:
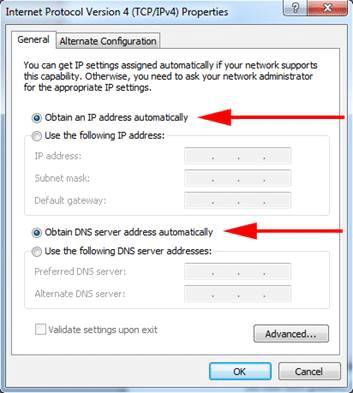
Clearing the static IPs is a simple matter at this point. Simply click the radio buttons labeled Obtain an IP address automatically and Obtain DNS server address automatically. This will clear out the address numbers. Make sure to click the OK button when finished.
At this point, it would be best to reboot the machine and try again to connect to a net-work and browse the internet. Hopefully, with your computer, notebook, notepad or smartphone free of static IP addresses, you will be free to browse the internet.
Technical Support Community
Free technical support is available for your desktops, laptops, printers, software usage and more, via our new community forum, where our tech support staff, or the Micro Center Community will be happy to answer your questions online.
Forums
Ask questions and get answers from our technical support team or our community.
PC Builds
Help in Choosing Parts
Troubleshooting
